Upgrades before second flight test
© NASA Kennedy Space Center / SpaceX, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The inaugural flight test of the fully integrated Starship and Super Heavy marked a significant stride in advancing the capabilities of the most potent launch system ever devised. This maiden voyage provided invaluable insights, directly driving upgrades to both the vehicle and ground infrastructure, enhancing the likelihood of future success. SpaceX’s hallmark rapid iterative development approach, pivotal in major innovations like Falcon, Dragon, and Starlink, underpinned this endeavour. Post-flight, SpaceX spearheaded the investigation with oversight from the FAA and collaborated with NASA and the National Transportation and Safety Board.
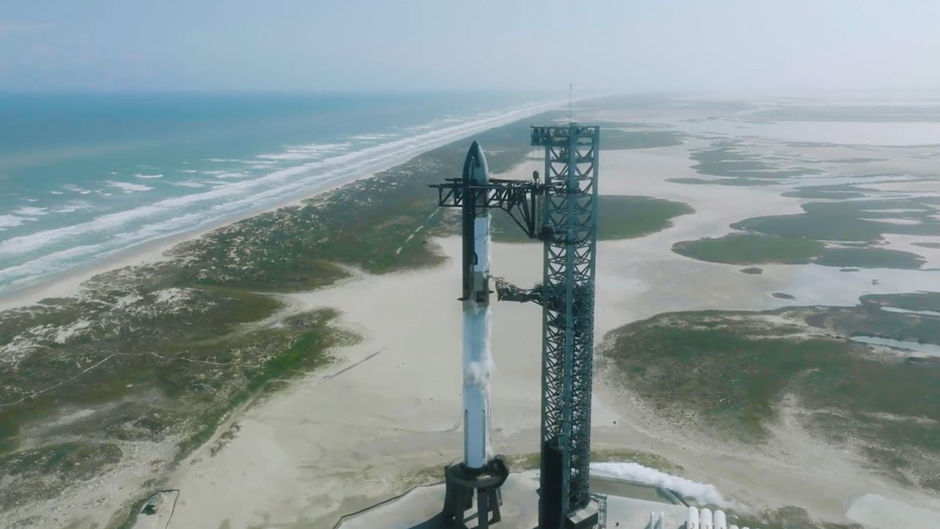

On April 20, 2023, at 8:33 a.m. CT (13:33:09 UTC), Starship and Super Heavy successfully lifted off from the orbital launch pad at Starbase in Texas, attaining a maximum altitude of ~39 km (24 mi) over the Gulf of Mexico. However, the ascent was not without challenges, as the vehicle experienced propellant leakage in the Super Heavy booster’s aft end, leading to a loss of communication and vehicle control. SpaceX swiftly implemented measures to address these issues, including enhanced testing and leak mitigation.
The Autonomous Flight Safety System (AFSS) executed a planned destruct command after deviations in trajectory, resulting in Starship’s breakup 237.474 seconds after engine ignition. SpaceX has since bolstered and reevaluated the AFSS to enhance its reliability.
SpaceX is implementing a comprehensive suite of system performance upgrades unrelated to the initial flight test issues. This includes the development and testing of a hot-stage separation system, allowing Starship’s second-stage engines to ignite and propel the ship away from the booster. Additionally, a new electronic Thrust Vector Control (TVC) system has been engineered for Super Heavy Raptor engines, employing fully electric motors for increased efficiency and reduced points of failure compared to traditional hydraulic systems.

Furthermore, substantial enhancements have been made to the orbital launch mount and pad system to prevent a recurrence of the foundation failure witnessed during the maiden flight test. These upgrades encompass reinforced pad foundations and the incorporation of a flame deflector, which has successfully undergone multiple tests.
Conducting hardware testing in a flight environment is paramount for swift learning and execution of design modifications and hardware enhancements, ultimately elevating the likelihood of success in future missions. The insights gained from Starship’s inaugural flight test have been invaluable, underlining the significance of iterative improvements in the pursuit of a fully reusable launch system capable of transporting satellites, payloads, crew, and cargo to a range of orbits and destinations, be it Earth, the Moon, or Mars.
On October 24, SpaceX successfully completed a crucial preflight test for its newest Starship prototype at the Starbase facility in South Texas. This “wet dress rehearsal” involved filling the Starship vehicle with cryogenic fuel to meticulously inspect for any potential leaks or issues before the upcoming flight. “Starship and Super Heavy were loaded with more than 10 million pounds of propellant today in a flight-like rehearsal ahead of launch,” On the night of October 24, SpaceX announced in a post on X.
“Vehicle is ready for the second test flight of a fully integrated Starship, pending regulatory approval,” In another post on X dated October 24, SpaceX stated.

Starship stands as the largest and most potent rocket ever constructed, with both of its stages engineered for complete and swift reusability. SpaceX’s Starship, a cutting-edge spacecraft, represents a pivotal leap in space exploration. Designed for missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, it boasts impressive capabilities. With a stainless steel structure and fully reusable design, Starship aims to mark a new era in space exploration.
SpaceX believes that the vehicle will revolutionize spaceflight, making a variety of bold exploration feats — including the human settlement of Mars, a long-held dream of Musk’s — economically feasible.